The Transformer model has emerged as a groundbreaking approach in natural language processing (NLP) and has revolutionized the field of machine learning. With its ability to process sequential data efficiently and capture long-range dependencies, the Transformer has paved the way for significant advancements in various NLP tasks. In this article, we will explore seven notable developments in Transformer model development.
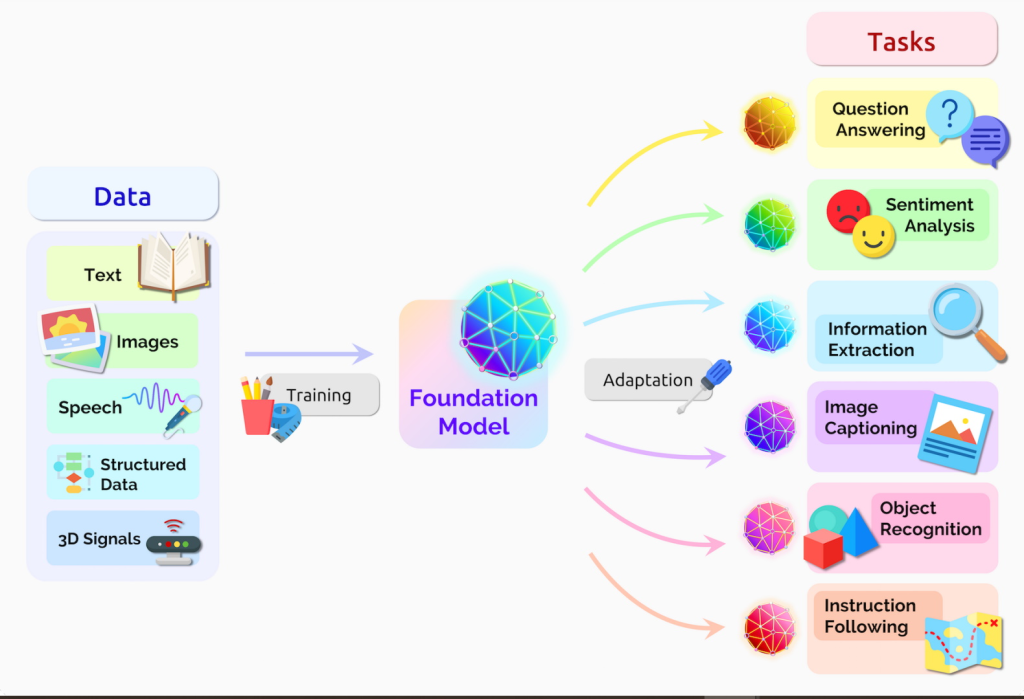
- Transformer Architecture: The original Transformer model introduced the self-attention mechanism, allowing the model to weigh the importance of different words in a sentence while processing it. The architecture comprised multiple self-attention layers and position-wise feed-forward networks, enabling effective representation learning for sequential data.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): BERT, introduced by Google AI, marked a significant milestone in NLP. It leveraged the Transformer model to pretrain a language model on a large corpus of unlabeled text and then fine-tuned it for specific downstream tasks. BERT achieved state-of-the-art results on various benchmarks, showcasing the power of the Transformer.
- GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer): OpenAI’s GPT took the concept of pretraining and fine-tuning to the next level. By training a Transformer model on a massive corpus of text and introducing a language modeling objective, GPT demonstrated impressive generation capabilities. It produced coherent and contextually relevant text, leading to applications like automated writing assistance and dialogue systems.
- Transformer-XL: One limitation of the original Transformer was its inability to handle long-range dependencies effectively. Transformer-XL, proposed by Google Brain, introduced a recurrence mechanism within the Transformer model, allowing it to capture dependencies beyond a fixed context window. This development enhanced the model’s ability to process longer sequences and led to better performance on tasks involving longer texts.
- XLNet: XLNet addressed the limitations of traditional autoregressive language models like GPT by introducing a permutation-based training scheme. By considering all possible permutations of words during pretraining, XLNet overcame the limitation of unidirectional context while maintaining the benefits of autoregressive models. This approach achieved state-of-the-art results on several language understanding benchmarks.
- T5 (Text-To-Text Transfer Transformer): T5, developed by Google Research, introduced a unified framework for NLP tasks. It demonstrated that a single Transformer model could be trained to perform various tasks, including text classification, machine translation, and summarization. T5’s approach of casting different tasks as text-to-text transformations showcased the versatility of the Transformer model.
- Efficient Transformers: Given the computational demands of Transformer models, researchers focused on developing more efficient variants. Approaches like Sparse Transformers and Performer reduced the memory and computational requirements of Transformers, making them more accessible for deployment on resource-constrained devices. These developments opened doors for real-time and on-device applications of Transformer models.
In conclusion, the development of Transformer models has transformed the landscape of NLP. From the original Transformer architecture to advancements like BERT, GPT, and various efficient variants, these models have significantly improved the state-of-the-art across a wide range of NLP tasks. With ongoing research and innovation, we can expect further exciting developments in the field of Transformer model development, enabling even more powerful and efficient natural language processing systems.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/transformer-model-development-services/