In the realm of artificial intelligence and natural language processing, the development of increasingly advanced models has been a constant journey. The Decision Transformer Model (DTM) stands as a testament to this progress, offering innovative approaches to decision-making and problem-solving that hold the potential to revolutionize various domains. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Decision Transformer Models, exploring their architecture, applications, and implications for the future of AI.
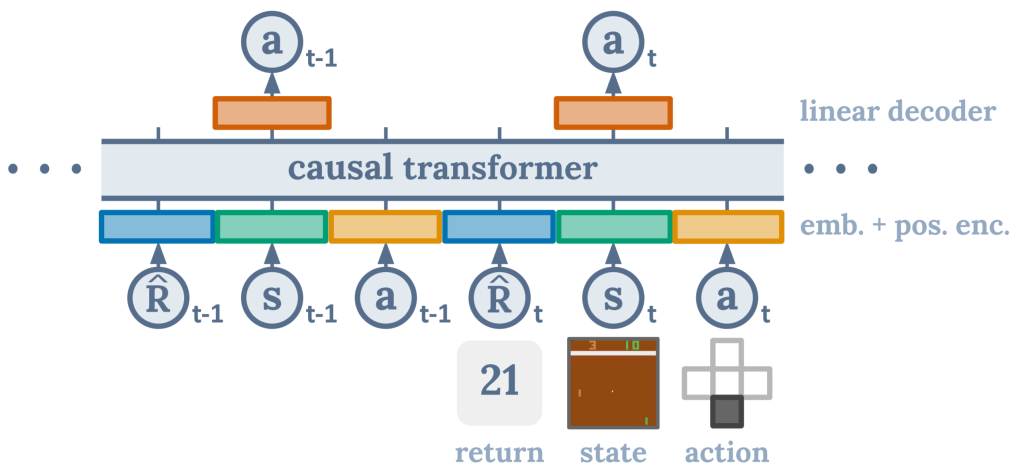
Understanding Decision Transformer Models
Decision Transformer Models, or DTM, are a specific class of machine learning models that aim to tackle a distinct challenge: sequential decision-making. While conventional transformers have excelled in processing and generating text or sequences, DTMs take this capability a step further by incorporating decision-making elements.
DTMs utilize a combination of reinforcement learning and deep neural networks to make decisions in a sequential manner. They integrate the ability to understand the context, generate actions, and assess their own decisions based on a given environment or task. In essence, DTMs can be thought of as transformers with built-in decision-making capabilities.
Architecture of Decision Transformer Models
The architecture of a Decision Transformer Model is rooted in its ability to process sequential data. It comprises several key components:
- Transformer Backbone: At the core of a DTM is a transformer-based architecture, which excels in capturing complex patterns and dependencies in sequential data. This architecture helps the model understand and contextualize the input information.
- Policy Network: The policy network, a crucial element of DTMs, is responsible for generating decisions or actions based on the input data. It utilizes the information processed by the transformer backbone to make choices.
- Value Network: In addition to generating decisions, DTMs often include a value network. This network helps the model assess the desirability of its decisions, enabling it to optimize its choices over time.
- Reinforcement Learning: To fine-tune its decision-making capabilities, DTMs often incorporate reinforcement learning techniques. This allows the model to learn from its own decisions and the rewards or penalties associated with them.
Applications of Decision Transformer Models
The versatility of Decision Transformer Models opens the door to a wide range of applications across different domains. Here are a few areas where DTMs are making significant strides:
- Natural Language Understanding: DTMs enhance natural language understanding by allowing AI systems to not only comprehend text but also generate coherent responses and take appropriate actions based on the conversation context.
- Robotics and Autonomous Systems: In robotics, DTMs enable more sophisticated decision-making for autonomous systems. Robots can navigate complex environments, adapt to changing conditions, and make intelligent choices in real-time.
- Healthcare: DTMs are being applied in healthcare for personalized treatment recommendations, disease diagnosis, and optimizing patient care plans by considering various factors and variables.
- Finance: In the financial sector, Decision Transformer Models are used for trading strategies, fraud detection, risk assessment, and portfolio management, where decisions need to be made sequentially in response to market dynamics.
- Gaming: In the world of gaming, DTMs have been used to create more dynamic and responsive non-player characters (NPCs) and enhance the player’s experience through AI-driven decision-making.
Challenges and Future Directions
While Decision Transformer Models hold tremendous promise, they also come with certain challenges. The training of DTMs can be computationally expensive, and ensuring they make ethical decisions remains a significant concern. Moreover, handling long sequences and incorporating real-world dynamics can be challenging for existing models.
The future of DTMs lies in addressing these challenges and further refining their architecture and training techniques. Ethical considerations and interpretability will continue to be at the forefront, as AI systems increasingly influence decision-making in critical domains like healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems.
Conclusion
Decision Transformer Models represent a remarkable advancement in the field of artificial intelligence, combining the strengths of transformers and reinforcement learning to make intelligent, context-aware decisions in sequential tasks. Their applications span various domains, and as research continues to evolve, we can expect Decision Transformer Models to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of AI-driven decision-making and problem-solving.