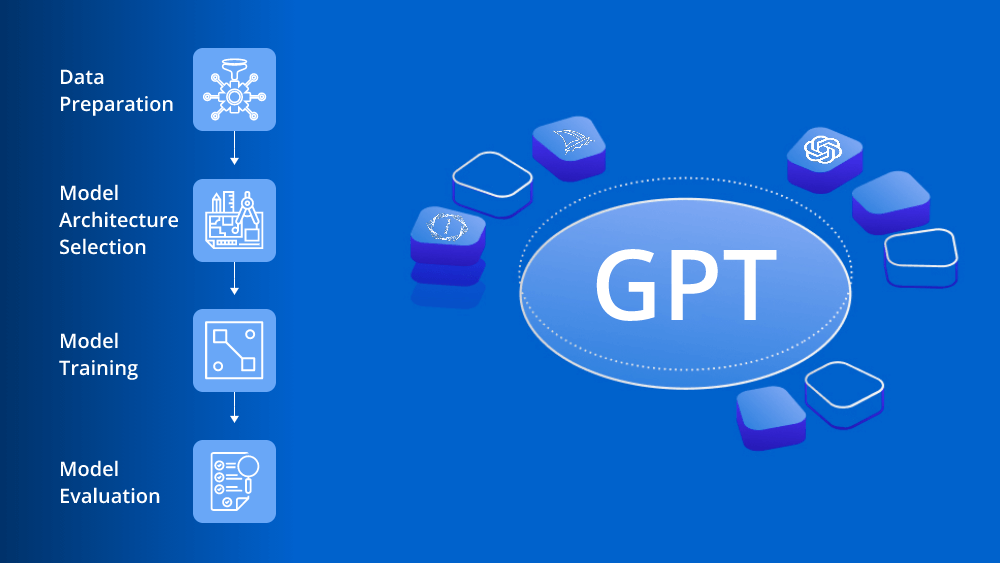
The realm of healthcare stands on the cusp of a technological revolution, with Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) emerging as a pioneering force, revolutionizing various facets of the industry. Leveraging advanced machine learning techniques, Generative AI has ushered in a new era marked by innovation, precision, and enhanced patient care across diverse healthcare domains.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
Generative AI has significantly elevated the accuracy and efficiency of medical imaging and diagnostics. Through Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and other deep learning models, AI systems analyze vast repositories of medical images such as MRIs, CT scans, and X-rays, aiding in early detection and diagnosis of diseases. These models can generate high-resolution images, improve image quality, and assist radiologists in identifying minute anomalies, thereby augmenting diagnostic accuracy.
Drug Discovery and Development
In the realm of pharmaceuticals, Generative AI has expedited drug discovery and development processes. AI-powered algorithms assist researchers in simulating molecular structures, predicting potential drug-target interactions, and generating novel compounds with specific therapeutic properties. By significantly reducing the time and resources required for preclinical testing, these models pave the way for the rapid development of innovative drugs and treatments.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Planning
The advent of Generative AI has paved the way for personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual patient profiles. Machine learning models analyze vast patient datasets, genetic information, and clinical records to create personalized treatment plans. These models predict patient responses to specific medications, optimize dosage regimens, and forecast disease progression, allowing healthcare providers to offer more targeted and effective therapies.
Natural Language Processing for Healthcare Records
Generative AI, particularly Natural Language Processing (NLP), has revolutionized the handling of healthcare records and documentation. NLP models comprehend and extract pertinent information from medical records, enabling efficient data management, automated coding, and improved interoperability across healthcare systems. This streamlines administrative processes, enhances accuracy, and facilitates better decision-making by healthcare professionals.
Virtual Health Assistants and Mental Health Support
Generative AI has transformed patient interactions through virtual health assistants and mental health support systems. AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants engage with patients, providing information, scheduling appointments, and offering mental health support. These assistants employ natural language understanding and generation, delivering empathetic and responsive interactions, thereby augmenting patient engagement and access to care.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
While the applications of Generative AI in healthcare are promising, ethical concerns regarding patient privacy, data security, and algorithm bias remain significant. Safeguarding sensitive patient information and ensuring unbiased AI-driven decisions are imperative for maintaining trust and integrity within healthcare systems.
Future Prospects
The trajectory of Generative AI in healthcare is poised for further advancements. Continued research and development will refine AI models, enhance predictive capabilities, and foster collaborations between AI technologies and healthcare professionals. The future holds promises of AI-driven innovations that could revolutionize disease prevention, treatment modalities, and healthcare delivery.
In conclusion, Generative AI stands as a transformative force in healthcare, revolutionizing diagnostics, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and patient care. While challenges persist, the collaborative efforts between AI innovators, healthcare practitioners, and regulatory bodies promise a future where AI technologies optimize healthcare outcomes, making quality care more accessible and tailored to individual needs.