In the rapidly evolving landscape of artificial intelligence and machine learning, organizations are increasingly leveraging the power of machine learning models to gain insights, automate processes, and make data-driven decisions. However, deploying machine learning models into production efficiently and maintaining them poses significant challenges. MLOps, short for Machine Learning Operations, is a set of practices that aims to bridge the gap between data science and operations to ensure a smooth and scalable deployment and management of machine learning models. In this article, we will explore a comprehensive guide on how to implement MLOps in points, covering the key steps and best practices.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration:
MLOps requires a strong collaboration between data scientists, software engineers, DevOps, and other stakeholders. Establish clear communication channels and shared responsibilities to promote a unified approach towards deploying and maintaining machine learning models. - Version Control:
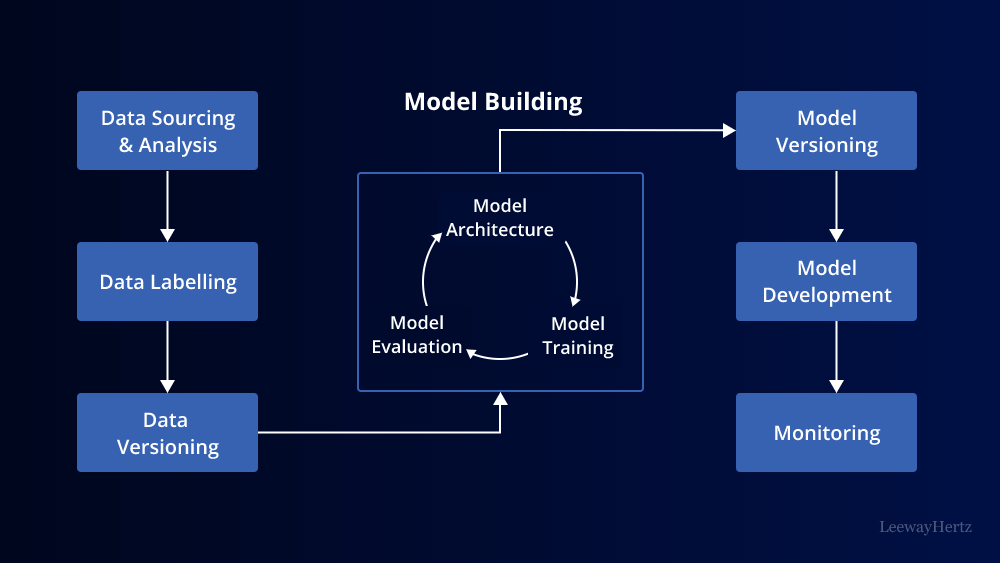
Implement version control systems such as Git to track changes to your machine learning code, datasets, and models. This ensures reproducibility, easy rollback, and collaboration between team members. - Automated Testing:
Adopt automated testing methodologies specific to machine learning models. Create unit tests for individual components, integration tests for the entire pipeline, and validation tests to ensure model performance meets the desired criteria. - Containerization:
Containerize your machine learning applications using platforms like Docker. Containerization streamlines deployment, improves consistency across environments, and simplifies scaling. - Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD):
Integrate CI/CD pipelines into your MLOps workflow to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying machine learning models. CI/CD ensures faster and error-free deployments, reducing the time-to-market. - Model Monitoring:
Implement monitoring solutions to track the performance of deployed models in real-time. Monitor metrics such as accuracy, latency, and resource utilization to detect anomalies and ensure models are functioning as expected. - Data Versioning and Lineage:
Track data changes and lineage throughout the machine learning pipeline. This helps in understanding model behavior, debugging, and maintaining data integrity. - Infrastructure Orchestration:
Utilize tools like Kubernetes to orchestrate containerized machine learning applications efficiently. Kubernetes enables automatic scaling, resource management, and fault tolerance. - Security and Governance:
Implement security measures to safeguard sensitive data and model intellectual property. Define access controls, encrypt data, and enforce data governance policies. - Model Explainability:
Ensure your machine learning models are interpretable and provide insights into their decision-making process. Explainable AI is crucial for building trust and meeting regulatory requirements. - Continuous Model Improvement:
Treat machine learning models as living entities. Continuously collect feedback, retrain models with updated data, and iteratively improve their performance. - Disaster Recovery and Rollbacks:
Have a robust disaster recovery plan in place to handle unforeseen issues. Define rollback strategies to revert to a stable model version in case of failures. - Documentation:
Thoroughly document each step of your MLOps process, including data preprocessing, feature engineering, model architecture, and deployment procedures. This documentation aids in troubleshooting, knowledge sharing, and onboarding new team members. - Feedback Loop:
Establish a feedback loop between data scientists and end-users. Gather feedback from stakeholders to identify areas of improvement and align model outputs with business needs. - Compliance and Ethics:
Adhere to ethical considerations and regulatory requirements when deploying machine learning models. Ensure models do not exhibit biased behavior and comply with relevant laws and regulations.
Conclusion:
MLOps plays a pivotal role in enabling organizations to harness the full potential of machine learning. By fostering collaboration, implementing automation, and adhering to best practices, businesses can deploy, monitor, and improve machine learning models efficiently and effectively. Embracing MLOps not only streamlines the development and deployment process but also ensures the long-term success of machine learning initiatives in an organization’s data-driven journey.
To Learn More:- https://www.leewayhertz.com/mlops-pipeline/