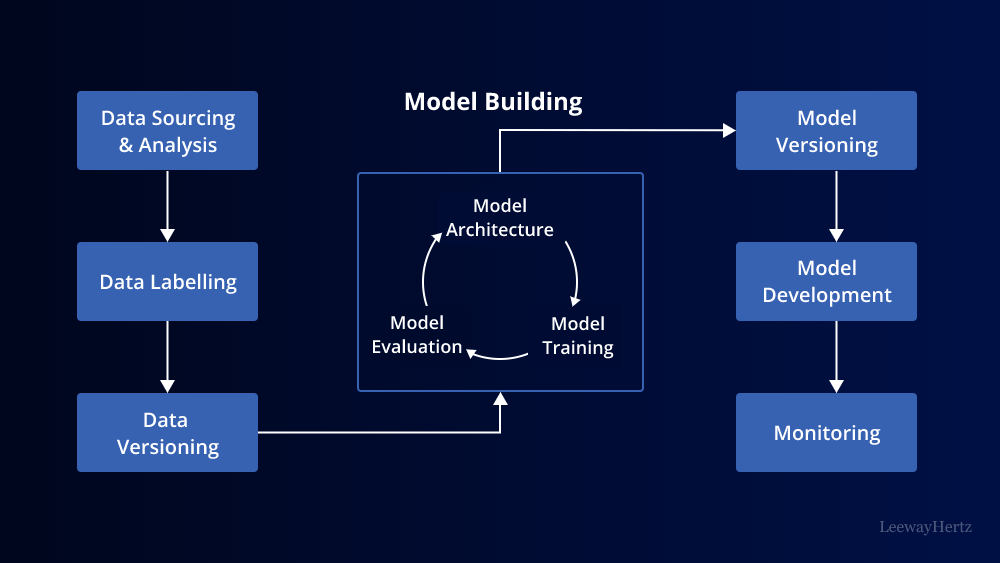
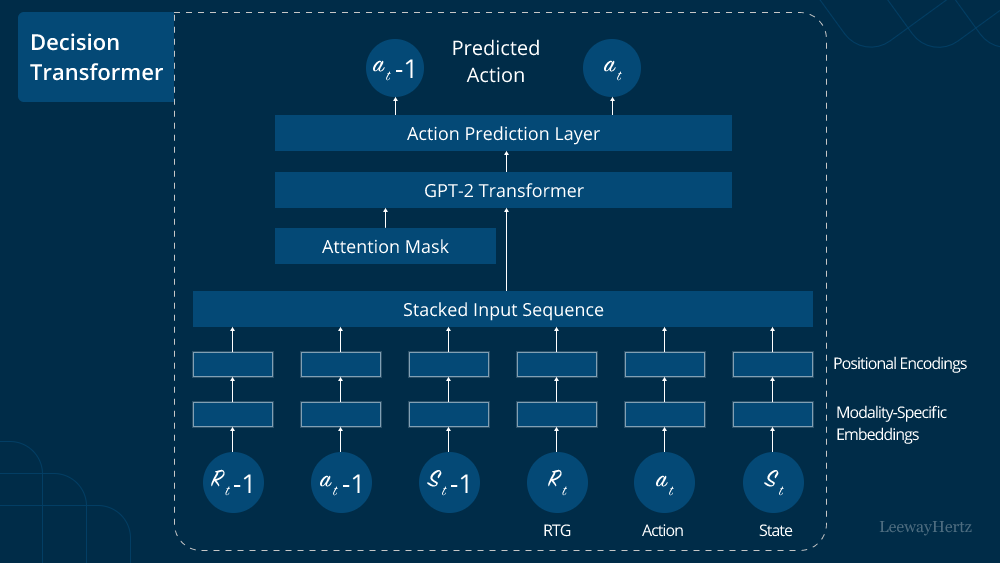
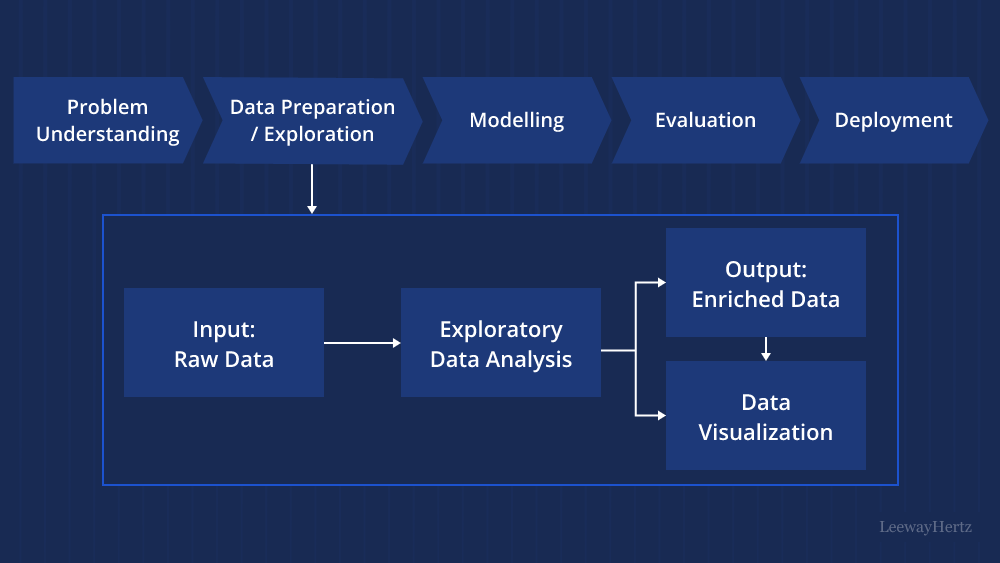
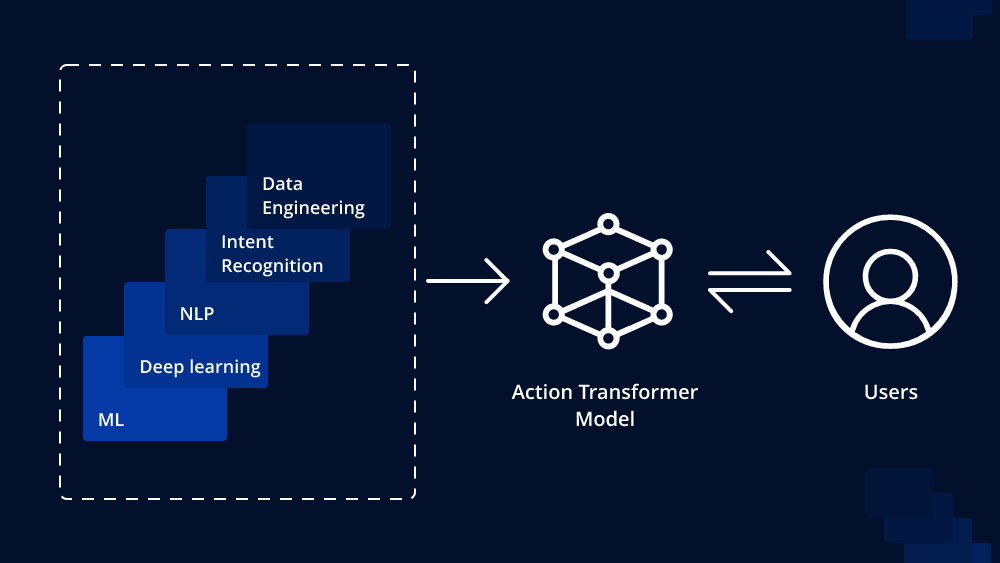
In the rapidly evolving landscape of AI development and consulting, one area that has captured the imagination of researchers, businesses, and creative minds alike is Generative AI. It’s a field that is pushing the boundaries of what machines can create, and it holds immense promise across various industries. In this article, we will embark on a journey into the exciting world of Generative AI development and consulting, exploring its fundamentals, applications, and significance in today’s technology-driven world.
I. Understanding Generative AI: The Foundation
Before we dive into the specifics, let’s start with the basics. Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the creation of content by machines. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on explicit rules and human-generated data, generative models can produce content autonomously. They have the ability to generate text, images, music, and even videos that, in many cases, are indistinguishable from those created by humans.
Generative AI achieves this feat through the use of neural networks, a concept inspired by the structure of the human brain. Neural networks consist of interconnected nodes, or artificial neurons, that process information in a way that allows them to learn patterns and make predictions. This ability to learn and create is at the heart of generative models.
II. Generative AI Applications: Beyond Imagination
One of the remarkable aspects of Generative AI is its wide range of applications, spanning across numerous domains. Let’s explore some of the most noteworthy areas where Generative AI is making a significant impact.
a. Creative Content Generation
- Imagine an AI system that can compose music in the style of Mozart or paint artworks reminiscent of Van Gogh. Generative AI has made such creative feats possible. It enables the generation of art, music, and literature that can rival the works of human creators.
b. Image and Video Synthesis
- In the world of image and video synthesis, Generative AI has transformed the gaming and entertainment industries. It can create realistic, high-resolution images and videos, opening up possibilities for realistic virtual environments and characters.
c. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
- In the realm of NLP, Generative AI has given rise to advanced chatbots and language models. These models can generate human-like text, making them invaluable in customer service, content generation, and even creative writing.
d. Healthcare
- Generative AI is aiding medical professionals by generating synthetic data for research and training purposes. It can also assist in medical image analysis, generating detailed reports from scans and helping in early disease detection.
e. Data Augmentation
- In data-driven fields like machine learning, Generative AI is used for data augmentation. It can generate synthetic data to expand small datasets, improving the performance of machine learning models.
III. The Significance of Generative AI in AI Development
Why is Generative AI development so significant in the world of AI? The answer lies in its potential to transform industries, disrupt traditional processes, and open up new avenues for innovation. Here are some key reasons why Generative AI is a must-know for AI developers and consultants:
a. Efficiency and Automation
- Generative AI can automate tasks that were previously time-consuming and labor-intensive. This automation not only saves time but also reduces the potential for human errors.
b. Creativity Amplification
- By harnessing Generative AI, businesses and individuals can amplify their creative capabilities. It can assist in generating content at scale, helping marketers, artists, and writers reach wider audiences.
c. Data Enhancement
- For AI developers, Generative AI offers a way to enhance and expand datasets, which is crucial for training robust machine learning models. This leads to improved AI system performance.
d. Personalization
- Generative AI can create highly personalized content and recommendations. This is invaluable for businesses looking to provide tailored experiences to their customers.
IV. Real-World Examples of Generative AI Success Stories
To illustrate the impact and potential of Generative AI, let’s explore a few real-world examples where it has already made significant contributions:
a. DeepArt.io
- DeepArt.io is an online platform that uses Generative AI to transform photos into famous art styles. It allows users to turn their ordinary photos into masterpieces reminiscent of famous painters.
b. OpenAI’s GPT-3
- OpenAI’s GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) is a language model that has taken the NLP world by storm. It can generate coherent and contextually relevant text, making it a versatile tool for content generation, chatbots, and more.
c. NVIDIA’s StyleGAN
- NVIDIA’s StyleGAN has set new standards for generating realistic images of human faces. It has been used in various applications, including the creation of deepfake videos and improving facial recognition technology.
V. Generative AI Consulting: Navigating the Opportunities
As Generative AI continues to evolve and find applications across diverse industries, it has created a growing demand for AI consulting services. AI consultants play a pivotal role in helping businesses leverage the power of Generative AI. Here are some key aspects to consider:
a. Customization
- AI consultants assess a client’s specific needs and customize Generative AI solutions accordingly. This might involve fine-tuning existing models or creating new ones from scratch.
b. Integration
- Integrating Generative AI into existing workflows and systems can be complex. Consultants facilitate this process, ensuring seamless integration and minimal disruptions.
c. Ethical Considerations
- Generative AI raises ethical concerns, particularly in the context of deepfakes and biased content generation. Consultants must navigate these issues and help clients develop responsible AI strategies.
d. Training and Support
- AI consultants provide training and ongoing support to ensure that clients can effectively use Generative AI tools and solutions.
VI. The Future of Generative AI Development
The journey into Generative AI development and consulting is just beginning. As we look ahead, it’s clear that this field will continue to evolve rapidly. Here are some key trends and developments to watch for in the future:
a. Improved Realism
- Generative AI models will become even more adept at creating content that is virtually indistinguishable from human-made content, leading to new opportunities in entertainment, marketing, and more.
b. Enhanced Personalization
- Generative AI will enable hyper-personalized experiences in various industries, from e-commerce to healthcare, as it becomes more skilled at understanding individual preferences.
c. Ethical Advancements
- As concerns over ethical issues grow, Generative AI will see advancements in ethical guidelines, content verification mechanisms, and safeguards against misuse.
d. Cross-Domain Applications
- Generative AI will find applications across diverse domains, including scientific research, design, and education, as it continues to break down barriers between different fields.
VII. Conclusion: Embracing Generative AI’s Potential
Generative AI development and consulting are at the forefront of technological innovation. Understanding the fundamentals, applications, and significance of Generative AI is not only beneficial but also essential for those in the AI development and consulting fields.
As we’ve explored in this article, Generative AI has already demonstrated its transformative potential in various sectors, from art and entertainment to healthcare and data science. AI consultants, in particular, are poised to play
a critical role in helping businesses navigate the opportunities and challenges presented by Generative AI.
The future promises even more exciting developments in Generative AI, and those who embrace this technology and its ethical considerations will be well-positioned to shape the AI landscape of tomorrow. So, whether you’re an AI developer, consultant, or simply curious about the future of technology, Generative AI is a journey worth embarking upon, as it unlocks new realms of creativity and possibility.
Building Blocks for Generative AI Development: Neural Networks and Frameworks
In our journey into the world of Generative AI development and consulting, we’ve already glimpsed the immense potential of this field and explored its wide-ranging applications. Now, it’s time to delve deeper into the foundational building blocks that empower Generative AI—neural networks and the frameworks that AI developers and consultants rely on. In this article, we’ll embark on a technical exploration, equipping you with the knowledge and tools necessary to harness the creative power of Generative AI.

I. The Power of Neural Networks
At the core of Generative AI lies the concept of neural networks. These computational constructs are inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain. Neural networks consist of interconnected nodes, also known as artificial neurons, organized in layers. The key to their functionality is their ability to process information, learn patterns, and make predictions. Let’s break down the components of neural networks and their role in Generative AI development:
a. Artificial Neurons (Nodes)
- Artificial neurons are the basic processing units of neural networks. They receive input signals, apply weights to those signals, and produce an output. These outputs are then passed on to other neurons, forming a network of interconnected processing units.
b. Layers
- Neural networks typically consist of multiple layers:
- Input Layer: This is where data is initially fed into the network.
- Hidden Layers: These layers perform the bulk of the computation and learning.
- Output Layer: This layer produces the final result or prediction.
c. Weights and Activation Functions
- Weights are assigned to connections between neurons, determining the strength of each connection. Activation functions introduce non-linearity into the model, allowing it to learn complex patterns.
d. Training and Learning
- Neural networks “learn” by adjusting their weights during a training process. This process involves feeding the network with labeled data and using optimization techniques like gradient descent to minimize prediction errors.
II. The Role of Frameworks in Generative AI Development
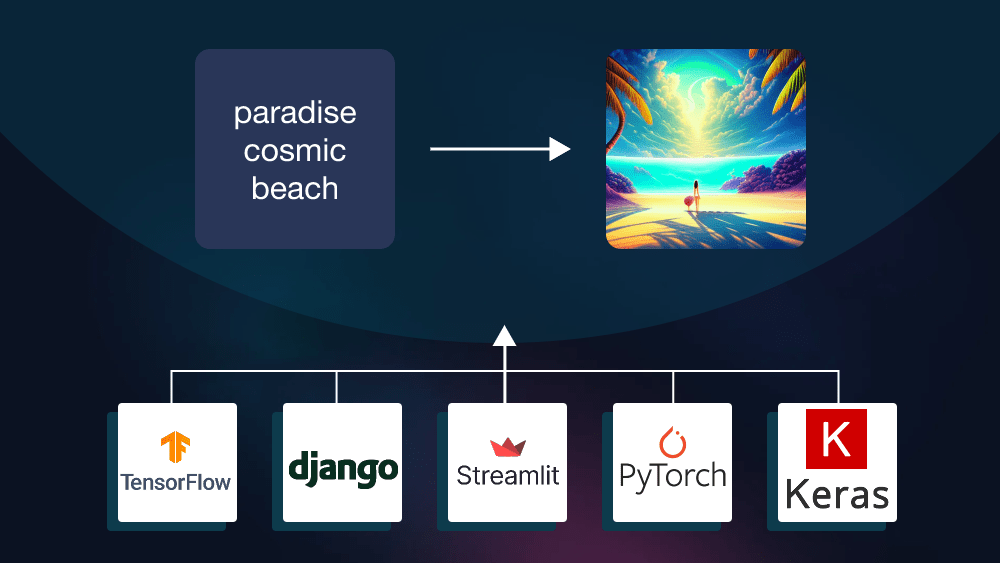
Now that we understand the fundamental components of neural networks, let’s explore the practical side of Generative AI development. Building and training neural networks from scratch can be a complex task. Fortunately, various frameworks and libraries have emerged to simplify this process. Here are some of the most prominent ones:
a. TensorFlow
- Developed by Google Brain, TensorFlow is an open-source deep learning framework known for its flexibility and scalability. It offers a high-level API called Keras, making it accessible for both beginners and experts. TensorFlow is widely used in Generative AI, particularly in the development of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs).
b. PyTorch
- PyTorch, developed by Facebook’s AI Research lab (FAIR), has gained popularity for its dynamic computation graph and ease of use. Its flexibility and intuitive design make it a favored choice for researchers and developers working on Generative AI projects.
c. Theano
- While not as popular today as TensorFlow and PyTorch, Theano played a crucial role in the early days of deep learning. It introduced concepts like automatic differentiation, which are fundamental to training neural networks.
d. Keras
- Originally a separate high-level library, Keras has been integrated into TensorFlow and serves as its official high-level API. Keras is known for its user-friendly interface, making it an excellent choice for those new to Generative AI development.
III. The Art of Generative AI Development
Generative AI development involves creating models that can generate content, whether it’s images, text, music, or any other form of data. Let’s take a closer look at how neural networks and frameworks come together in the development process:
a. Data Preparation
- Before diving into model development, a crucial step is data preparation. High-quality and diverse datasets are essential for training effective Generative AI models. This data can come from various sources, such as images, text, or audio recordings.
b. Model Architecture
- The choice of neural network architecture depends on the specific generative task. For image generation, architectures like the Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) or Variational Autoencoder (VAE) are commonly used. Text generation may require recurrent neural networks (RNNs) or Transformers.
c. Hyperparameter Tuning
- Neural networks have various hyperparameters that require fine-tuning to achieve optimal performance. These include learning rates, batch sizes, and the number of layers in the network. Experimentation and iteration are key to finding the right set of hyperparameters.
d. Training Process
- Training a Generative AI model involves feeding it with data and iteratively adjusting its internal parameters (weights) to minimize a loss function. The training process can take time, depending on the complexity of the model and the size of the dataset.
IV. The Role of Generative AI in AI Consulting
Generative AI is not only a technological marvel but also a valuable tool for AI consultants. Here’s how AI consulting services can benefit from Generative AI:
a. Custom Solutions
- AI consultants assess their client’s specific needs and design custom Generative AI solutions. This could involve tailoring existing models or creating entirely new ones to address unique challenges.
b. Integration Expertise
- Integrating Generative AI into existing workflows can be complex. AI consultants provide expertise in seamlessly integrating Generative AI solutions into their client’s systems and processes.
c. Ethical Considerations
- The responsible use of Generative AI is crucial. Consultants help clients navigate the ethical considerations surrounding AI-generated content and provide guidance on adhering to ethical standards.
d. Training and Support
- AI consultants offer training and ongoing support to ensure clients can effectively use Generative AI tools and solutions. This includes educating staff and troubleshooting issues that may arise.
V. Challenges and Considerations in Generative AI Development
While Generative AI offers immense potential, it also comes with its share of challenges and considerations:
a. Data Quality and Quantity
- High-quality and diverse training data is essential for Generative AI. In some cases, obtaining such data can be a significant challenge.
b. Ethical Concerns
- As mentioned earlier, Generative AI can be used unethically to create deepfake content or generate biased outputs. Ensuring ethical use and mitigating these risks is a top priority.
c. Computational Resources
- Training large Generative AI models can be computationally intensive and require powerful hardware, which may not be accessible to everyone.
d. Interpretability
- Understanding how a Generative AI model arrives at a specific output can be challenging, making it important to develop methods for model interpretability.
VI. Conclusion: Empowering Generative AI Development
As we conclude our exploration of the building blocks of Generative AI, it’s evident that this field represents a convergence of technology, creativity, and innovation. Neural networks, supported by frameworks, serve as the engine behind Generative AI’s ability to create, design, and inspire.
For AI developers, consultants, and enthusiasts, understanding these building blocks is not just a matter of technical knowledge—it’s a gateway to unlocking new frontiers of possibility. With the right tools and expertise, Generative AI has the potential to reshape industries, elevate creative endeavors, and address complex challenges in ways that were previously unimaginable. As the field of
Generative AI continues to evolve, those who master its intricacies will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of artificial intelligence.
Elevating Your AI Consulting with GANs: Generative Adversarial Networks Demystified
In the dynamic landscape of AI development and consulting, staying at the forefront of innovation is key to success. One technology that has captured the imagination of both developers and consultants alike is Generative Adversarial Networks, or GANs. These remarkable neural networks have the potential to transform the way we approach AI consulting services, offering new avenues for creative problem-solving and generating content with unparalleled realism. In this article, we will demystify GANs, explore their inner workings, and discuss their vast array of applications, highlighting their significance in the world of AI consulting.

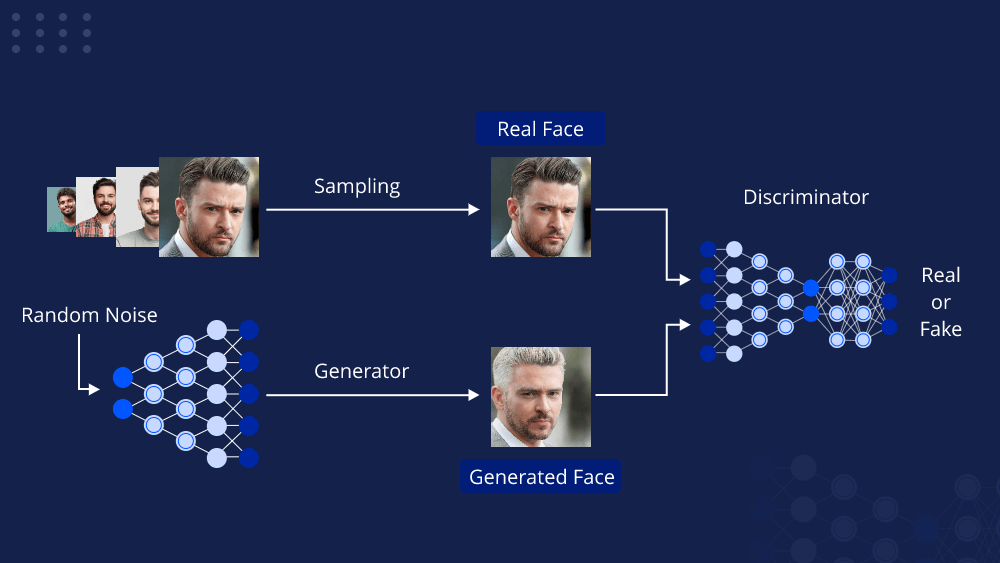
I. Decoding Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
At the heart of GANs is a fascinating concept: pitting two neural networks against each other in a competitive process. This adversarial nature is the foundation of their power. Let’s delve into the core elements of GANs:
a. The Generator
- The generator network’s role is to create content. It starts with random noise as input and gradually refines its output until it becomes indistinguishable from real data. This iterative process is akin to an artist honing their craft.
b. The Discriminator
- The discriminator network acts as a critic. It evaluates the content generated by the generator and distinguishes between real and fake data. It’s like a vigilant art critic trying to spot counterfeit masterpieces.
c. The Adversarial Training Process
- GANs operate through an adversarial training process where the generator and discriminator continuously compete against each other. The generator aims to improve its output to deceive the discriminator, while the discriminator strives to become better at distinguishing real from fake data.
d. Equilibrium and Realistic Output
- When GANs reach equilibrium, the generator produces content that is so realistic that it becomes difficult for the discriminator to tell it apart from genuine data. This is where GANs truly shine, as they create content that is virtually indistinguishable from human-made data.
II. Real-World Applications of GANs in AI Consulting
GANs are not just theoretical constructs; they have practical applications across various industries. As AI consultants, understanding these applications can unlock new possibilities for your clients. Here are some notable use cases:
a. Image Generation and Enhancement
- GANs can create high-quality images, which find applications in industries like fashion, interior design, and product prototyping. AI consultants can offer clients solutions for generating realistic product images and enhancing photo quality.
b. Style Transfer
- GANs excel at transferring styles from one image to another. This is valuable in fields such as graphic design and marketing, allowing for the creation of unique visual content.
c. Data Augmentation
- AI consultants can use GANs to augment datasets, which is crucial in training machine learning models with limited data. This technique enhances model performance across various domains, from healthcare to finance.
d. Anomaly Detection
- GANs can be employed for anomaly detection in large datasets. AI consultants can leverage this capability to help clients identify and mitigate potential issues in their operations.
e. Face Generation
- GANs have been used to generate realistic human faces, which can be valuable in identity verification, virtual reality, and entertainment.
III. GAN Variants and Specializations
The GAN framework is incredibly versatile, and over time, various specialized GAN variants have emerged, each tailored to specific tasks and industries. Here are some notable GAN variants:
a. Conditional GANs (cGANs)
- cGANs take additional input, known as conditional data, to generate content with specific characteristics. These are valuable for tasks like image-to-image translation and data synthesis with specific attributes.
b. CycleGAN
- CycleGANs are used for unpaired image-to-image translation. They learn to convert images from one domain to another without direct matching pairs, making them suitable for various creative applications.
c. DCGAN (Deep Convolutional GAN)
- DCGANs leverage deep convolutional neural networks for image generation. They are known for producing high-resolution, realistic images and are widely used in AI consulting projects involving image synthesis.
d. StyleGAN
- StyleGANs are renowned for their ability to generate highly detailed and customizable images. They allow users to control specific aspects of the generated content, making them suitable for creative applications.
IV. Ethical Considerations and Responsible GAN Usage
While GANs offer incredible creative and practical potential, their power also comes with ethical responsibilities. As AI consultants, it’s essential to be mindful of these considerations:
a. Deepfakes
- GANs can be used to create convincing deepfake videos, which have raised concerns about misinformation and privacy. AI consultants should be aware of these issues and help clients use GANs responsibly.
b. Bias and Fairness
- GANs can inherit biases present in their training data. Consultants must be diligent in addressing bias and ensuring fairness when deploying GAN-generated content.
c. Verification and Authentication
- The ability of GANs to create highly realistic content raises challenges in content verification and authentication. Consultants should guide clients in developing robust methods for verifying GAN-generated content.
d. Regulation and Compliance
- As GANs become more powerful, regulatory bodies may introduce rules and regulations governing their use. AI consultants should stay informed about legal and compliance considerations related to GANs.
V. GANs in AI Consulting: Navigating Opportunities
As an AI consultant, incorporating GANs into your consulting services can be a strategic move. Here’s how GANs can enhance your offerings:
a. Customized Content Generation
- GANs enable AI consultants to offer customized content generation solutions to clients, whether it’s for marketing materials, product design, or data augmentation.
b. Enhanced Data Quality
- Consultants can use GANs to improve data quality by generating synthetic data to fill gaps in existing datasets, leading to more accurate machine learning models.
c. Creative Solutions
- GANs can spark creativity by generating innovative content and designs. AI consultants can leverage this creativity to provide unique solutions to their clients’ challenges.
d. Anomaly Detection Services
- GANs can be employed for anomaly detection, a valuable service for clients seeking to identify irregularities in their data.
VI. The Future of GANs in AI Consulting
As we look to the future, the role of GANs in AI consulting is likely to expand. Here are some trends and developments to watch for:
a. Improved Realism
- GANs will continue to produce content with ever-increasing realism, further blurring the lines between human and machine-generated content.
b. Interdisciplinary Applications
- GANs will find applications across various domains, including art, science, and entertainment, as they become integrated into the creative process.
c. Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
- The ethical and regulatory landscape surrounding GANs will evolve. AI consultants will play a pivotal role in guiding clients through these changes.
d. Enhanced Creativity
- GANs will empower creators to explore new dimensions of creativity, allowing for the generation of content that was previously unimaginable.
VII. Conclusion: GANs – Transforming AI Consulting
In conclusion, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are a remarkable addition to the toolkit of AI consultants. Their ability to generate content with stunning realism opens up a world of possibilities across diverse industries. However, with great power comes great responsibility, and AI consultants must navigate ethical considerations and ensure responsible usage.
By incorporating GANs into their consulting services, AI consultants can provide innovative, customized solutions to their clients’ challenges, from content generation to data augmentation and anomaly detection. As GAN technology continues to advance, those who embrace it will be at the forefront of AI consulting, shaping the future of creative problem-solving and content generation in a rapidly evolving world.